If you are suffering from diabetes, you and your doctor have likely already discussed your diet plan, exercise regime and other self-help things you can do to keep your diabetes under control. Indeed, in diabetes treatment adherence to a strict diet and exercise regime is seen as being equally as important as insulin therapy or medication to avoid complications. Here is a guide to some of the common treatments available as well what you can do at home.
In our section on Diabetes treatments, get all of the information you need to keep your diabetes under control. Check out our articles on Insulin, insulin issues, metformin, weight gain and diabetes, and diet and diabetes. Start feeling better today.
Self-Care Treatments
Once diagnosed with diabetes, there are many things you can do for yourself to keep your diabetes under control. There include incorporating the following into your daily routine:
Follow a Diabetes Diet
The advantages of a healthy diet are numerous and that is why from the diagnosis of your disease to its lifelong treatment, your doctor will always stress good food habits and give you a diabetes diet to follow.
This is because what you eat and how much you eat has an effect on the blood sugar level of your body. When you eat a meal rich in fibers, low in fat or sugar, and with a regular calorie count during all meal times, the body can balance sugar levels much easier than if what you eat varies dramatically from meal to meal. If you are taking insulin or medications, the diet will ensure that these do not have any adverse effects on the sugar level of your body. Furthermore, sticking to a proper diabetic diet helps you remain more active and fight off other illnesses you can become susceptible to.
In truth, diabetes diets are not drastically different from the average healthy diet recommended for everyone. In other words, you won’t be doomed to eating bland, tasteless food with abundance of boiled vegetables. It is only a balanced meal that is rich in nutrients while at the same time avoiding too much sugar or fat. If you’re having trouble becoming inspired, use the internet and local cook book store for ideas.
Exercise
Regular, moderate exercise is good for a diabetic as it helps keep the blood sugar level under control. In addition, exercise and physical activities help in keeping your weight under control, as obesity can further complicate your diabetes.
You may choose anything from walking, cycling, jogging, aerobics or yoga but do remember to consult your doctor about your exercise regime. It is vital that you ensure you are not exercising more than necessary, as excessive activity can cause your blood sugar levels to fluctuate dangerously, which can actually be life threatening.
If exercise is something you are starting only after the diagnosis of the disease, remember to start slow and build your strength gradually. Doing 30 minutes of moderate exercise a few times a week is a good staring point, and will definitely be beneficial while not being overly stressful.
And remember that getting your exercise doesn’t always mean going to the gym; gardening, walking up the stairs, cooking, washing etc. all count as physical activity.
Limit Alcohol
Alcohol intake should be very limited for diabetics, as it causes an increase in blood sugar level, triglyceride fats and may even cause nerve pain. If you do want a drink, limit yourself to 1-2 drinks in an evening.
Stop Smoking
You likely already know the harmful effects of smoking, including lung cancer. But if you are diabetic, you need to be all the more careful as smoking can damage blood vessels, cause strokes, heart problems and circulation problems.
Monitor Your Blood Glucose
As a diabetes patient it will be helpful for you if you can monitor your blood glucose level on your own. This will let you know the exact condition you are in at a particular time and also know the effect of diet, medicines etc. on your health and blood sugar level. If your blood sugar level does not decrease in spite of the treatment you can ask your doctor to make the necessary changes.
How often you will need to monitor your glucose levels will depend on the type of diabetes you have as well as your age and any other complications you may have.
Medical Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes
With type 1 diabetes the body cannot make insulin on its own and thus the treatment involves insulin therapy, usually with an injection or an insulin pump.
You may be given a combination of long acting and fast acting insulin doses; the dosage itself depends on the severity of your case. During mealtimes your dosage may be increased to cope with the additional sugar the body has to break down at this time. Insulin cannot be taken orally as then it gets destroyed in the stomach.
When you are given insulin, you must be sure to eat something, as the chemical will act on glucose even if you have not taken your meal. This may suddenly lower your glucose level and put your health at risk. Maintaining a daily record of your dosage, meal times and type of meal, as well as your exercise routine will help you understand the affect of insulin on your body and also give the doctor the proper knowledge of how treatment is helping your diabetes.
Medical Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes
In this type of diabetes condition has a resistance to insulin and cannot use it properly to breakdown glucose into energy. Thus initially when you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, insulin therapy is not an option. Rather your doctor will stress more self-help treatments like diet and exercise and also medications that help the body in breaking down sugars.
Some of the medications for diabetes are:
- Sulfonylureas: This drug stimulates the pancreas to make more insulin. However it may cause low blood sugar.
- Biguanides: Metformin is a type of biguanide that is mostly prescribed in the United States. This drug inhibits the production or the release of sugar from the liver and thus you need less amounts of insulin in your body. Biguanides have also been known to cause less weight gain than other medications. The side effects may be nausea, vomiting, gas, abdominal pain etc.
- Meglitinides: They have an effect similar to sulfonylrea without the side effect of lowering blood sugar.
- Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: These drugs work by blocking the action of the enzymes that breakdown carbohydrates. As a result the blood absorbs sugars more slowly and a rapid rise in blood sugar levels just after a meal is prevented. It may cause abdominal bloating or diarrhea.
- Thiazolidinediones: These medicines act in two ways. They make the body tissues more sensitive to insulin and they also make the liver produce less sugar. As these medicines have been known to cause liver damage, however, you should get your liver checked every 2-3 months. Other side effects may be weight gain and fatigue.
For type 2 diabetes a combination of drugs may be given to you depending on your case, and many people may also need insulin with age as the body’s insulin production becomes lesser and lesser.
Regardless of how severe your condition is, you may want to change to online ordering when obtaining these medications. Arguably the most important benefit is that the medicine is delivered directly to your home, which means that you never have to worry about finding a way to go to the drug store when it runs out.
Further, there are a plethora of excellent deals online, and you can often save a significant amount of cash by ordering in bulk. For these reasons alone, it is certainly worth your time, health, and money to investigate this new and convenient service.
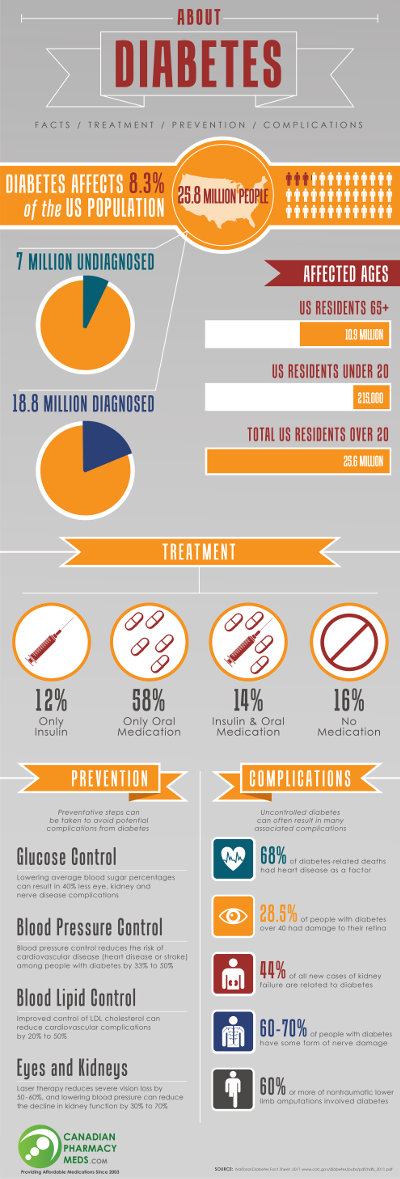
Diabetes: Facts, Treatment and Prevention
Transplantations
Modern medical advances have brought transplantations, like a pancreas transplant for those suffering from type 1 diabetes, to the fore. Pancreas transplants are mostly preformed on people who are already getting a kidney transplant.
This may help them get totally diabetes free and without the need insulin. But pancreas transplants are many times unsuccessful as you body may try to reject the new organ. If you are interested in this option do ask your doctor as the transplant may involve more risk than simply caring for diabetes in the long-term.
Islet cell transplantation is another option doctors are looking into nowadays which is less risky, less expensive and provides a better chance of the body’s adaptation to the new organ. In the pancreas there are actually hundreds of islet cells that produce insulin. In the transplantation the doctors infuse fresh islet cells into the liver where they spread and start producing insulin. However, this procedure is still under research.